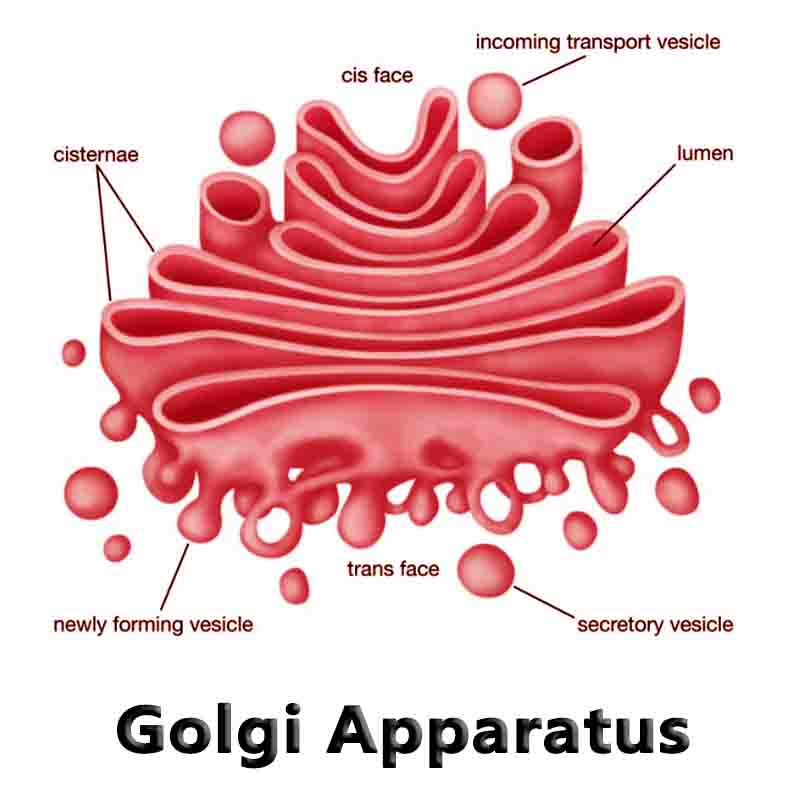
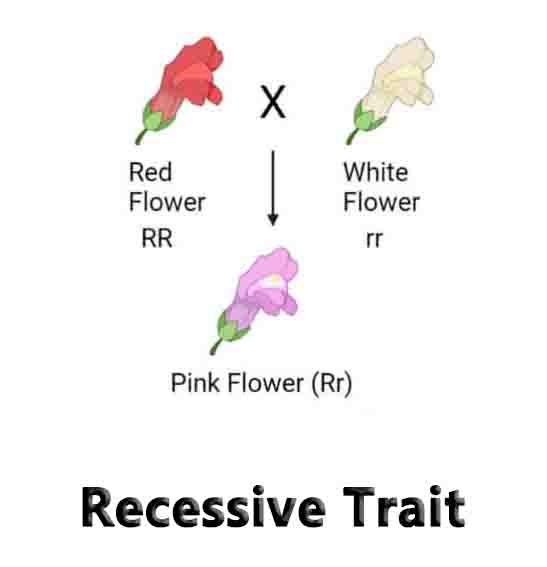
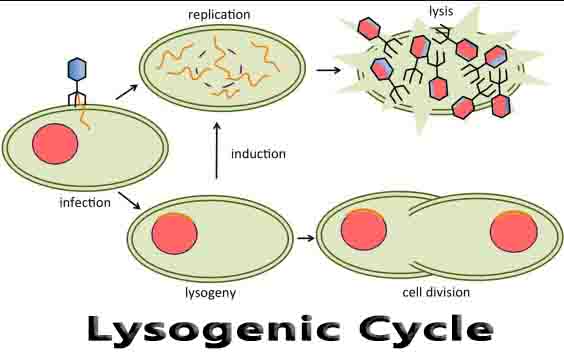
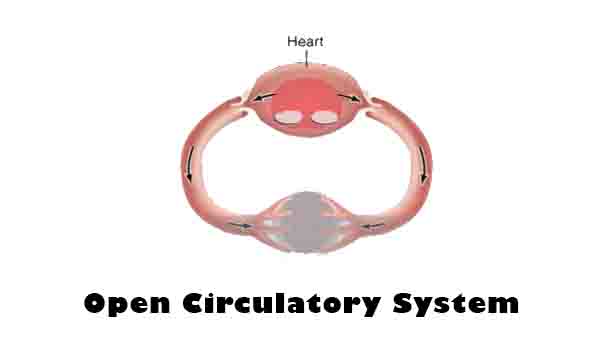
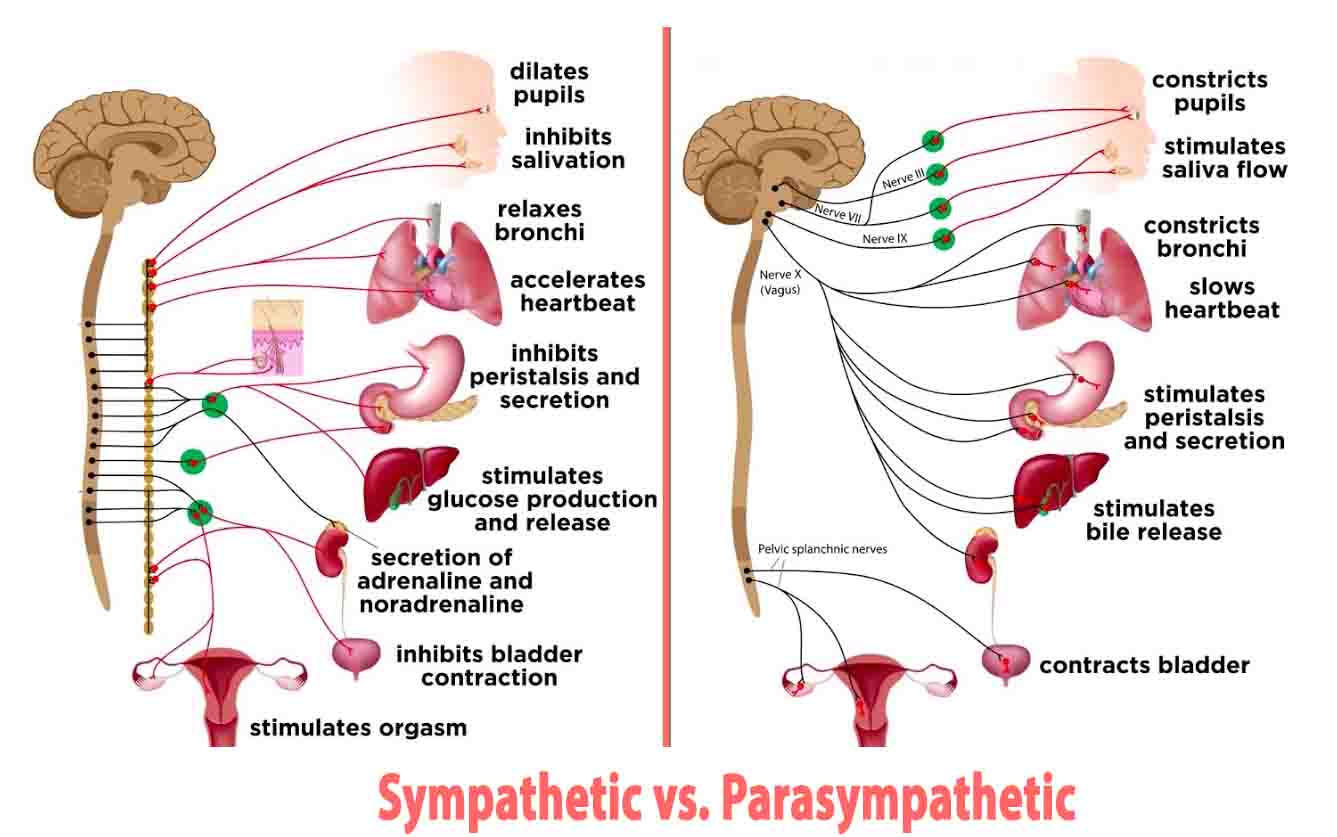
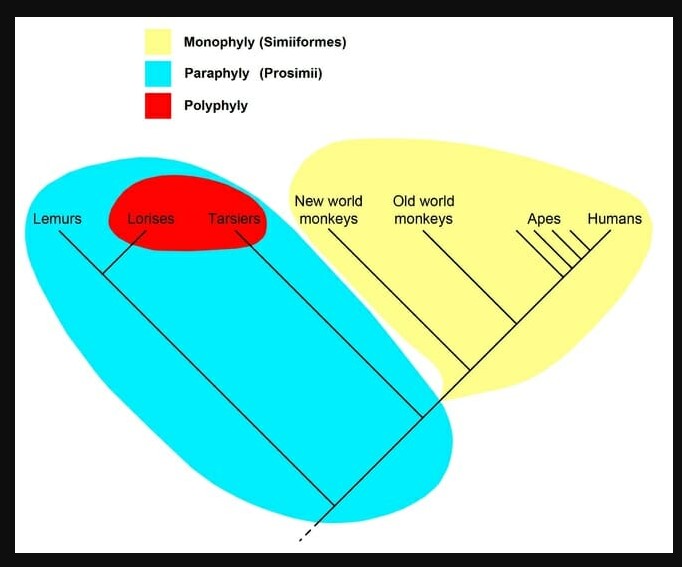
Detritivore
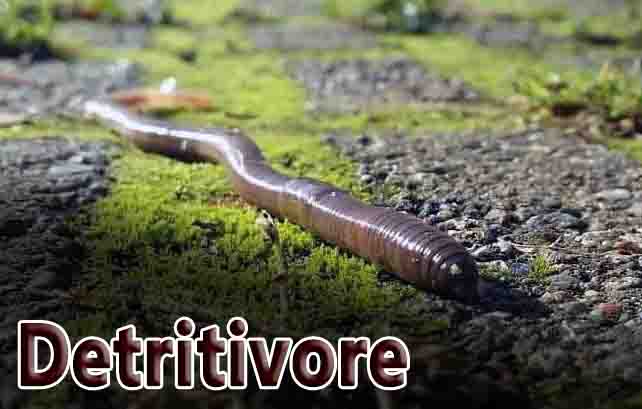
Detritivore Definition Detritivores obtain their nutrition by feeding on detritus, which is a heterotrophic organism. Detritus consists of dead plants and animals. Alternatively, detritivores may consume feces for nutrition, a feeding strategy called coprophagy. Invertebrates such as mites, beetles, butterflies, and flies; mollusks such as slugs and snails; or soil-dwelling earthworms, millipedes, and woodlice are … Read more